Game Testing: Is it Really Necessary?
Experts from Braze, a mobile engagement automation company, define QA as a ‘key brand differentiator’. Quality improvements influence user experience and engagement, which are the key factors of game popularity.
CleverTap shares that “25% of all apps are only used once” and “a 10% increase in user retention can increase the value of a business by more than 30%”.
So, what can game developers do to increase user retention? Every stage of the game dev process contributes to user happiness, but QA should not be overlooked. Moreover, only 29% of tech companies perform exploratory testing, (QA tests the product while it’s being developed, not after full completion).
Both developer-based testing and QA can alleviate commercial release bottlenecks, downtime on production, and decrease the number of significant game defects. Efficient and thorough QA will ensure a successful release and increase user retention.
Here are some examples of failed games that demonstrate why testing is important:
- Ni no Kuni II, with a lack of voiced dialogues, this was a dull and disappointing release;
- Vampyr, a disorganized game which was criticized by users for its complex battles;
- Vane, glitchy mechanics and annoying design was a disappointment for many users.
A lot of features are critical for a fun product: music, sounds, graphics, dialogues, and more. If you don’t want to release a boring game with poor user engagement, QA must be a mandatory stage in your product software development lifecycle.
What is game testing and its place in the game development lifecycle?
An idea or concept is generally the starting point for any product. But what happens next?
Irme Jele, a co-founder of Bossa Studios says, “You can make an amazing game, but you can’t make a success. Your players make the success.” Keeping the users’ wants and needs in mind through the entire game dev process is vital to the success of your game.
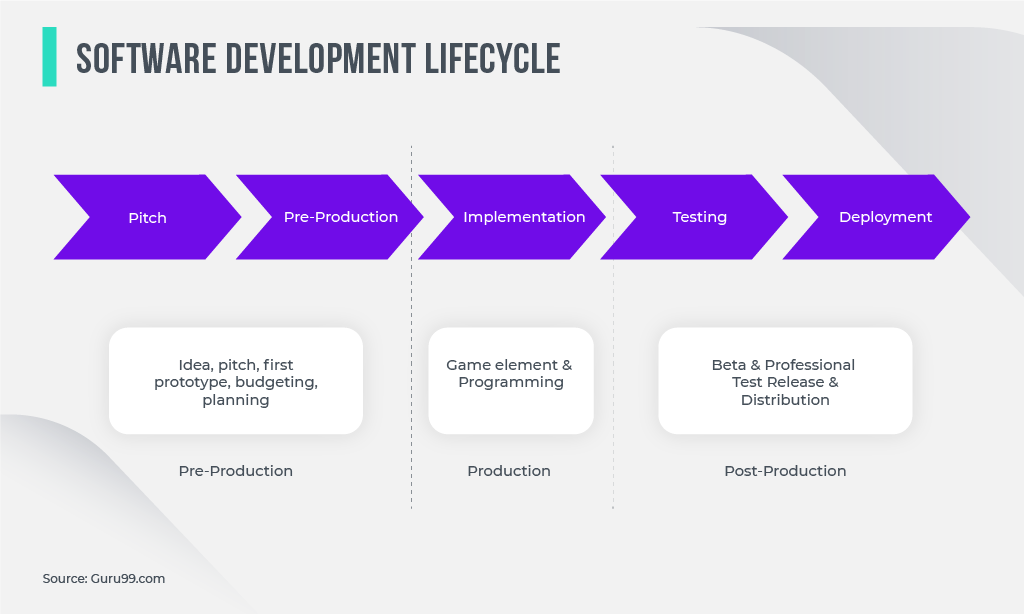
Game testing is imperative for quality management and finding bugs. Testing is needed during the development cycle in order to be ready for the Alpha launch, an early version with potential for many mistakes.
During testing, QA engineers must find answers to the following questions:
- whether the character can or can’t complete the activities foreseen by the script;
- if the character is unable to overcome obstacles;
- which dialogues are boring or not clear enough;
- whether the rules or levels are too complicated (or easy and not engaging);
- is there a ‘fun factor’ (whether it is satisfying enough when completed fully).
Answering these questions is indispensable to understanding every nuance of your game before Alpha and Beta releases. That is why QA is an essential piece of the puzzle in the game development lifecycle along with:
- Planning and discovery stage: GDD (game design document) is created. In this document, production team outlines game mechanics and rules as well as future design;
- Production is a time and resource-consuming stage. The goal here is to thoroughly render every component of the game (scenes, characters, levels, scenarios) on the screen. During this stage continuous iterations and exploratory testing are performed;
- Testing for quality control targets identifying bugs, ensuring smooth gameplay and clarity of rules (or levels completion). Sometimes a bug sheet is delivered to the devs as an outcome of this game development stage;
- Pre-launch in game development is an important milestone as it is both the testing and marketing stage to help the users get acquainted with the product before the Beta version is released. It’s a good chance to learn player feedback as well as to present the game at famous international industry events: E3 (The Electronic Entertainment Expo — annual trade fair) or PAX (Penny Arcade Expo — series of game cultural festivals);
- Launch (release) takes place when the game code is clean and QA engineers complete the bug sheet;
- Post-launch is an exciting period of enjoying the fruits of your labor, but it’s also a time to update the released game and continue testing. Post-launch support includes continuous monitoring of user feedback and bug reports. Then, DLCs are issued (which is game downloadable additional content) and game patches are delivered by the development team.
The game development process takes a lot of time and demands several iterations, thorough testing, launching Alpha and Beta versions and many hours of behind-the-scenes work.
Every stage involves testing: exploratory testing throughout the whole development process, clean room procedures to assure code reliability, and users’ post-production reports as a kind of testing as well.
Game Testing: The Complete Overview of Stages, Techniques, Processes, and Approaches
Marissa Mayer, the Yahoo CEO, noticed in her Twitter: ‘Geeks love tech issues so much, that all the details are of crucial importance’. This quote is relevant to our topic as well. Assuring game quality we exclude irritating bugs and errors spoiling nice game concepts. So, what stages should be followed to create the perfect product?
What are the stages of game testing?
We propose to follow every stage to learn about objectives, responsible specialists, and the sense of the procedure.
Stage: closed Alpha testing takes place on the preliminary level
Objective: identify bugs, which were not obvious in the earlier development stages
Who performs: a group of users reflecting the real user environment and playing as if it happens in real life after the game release.
Stage: closed Beta. It’s quite similar to closed Alpha but more extensive
Objective: figure out the potential obstacles to the natural smooth playing flow
Who performs: volunteers from the users, not development team members
Stage: open Beta is a stage, during which all users are welcome to play the game and report any poor functionalities
Objective: improve user experience and define any broken code in a production environment
Who performs: every user willing to play
Stage: Fun factor, balance, learnability, or reliability tests
Objective: make live user test process successful
Who performs: real players or focus groups
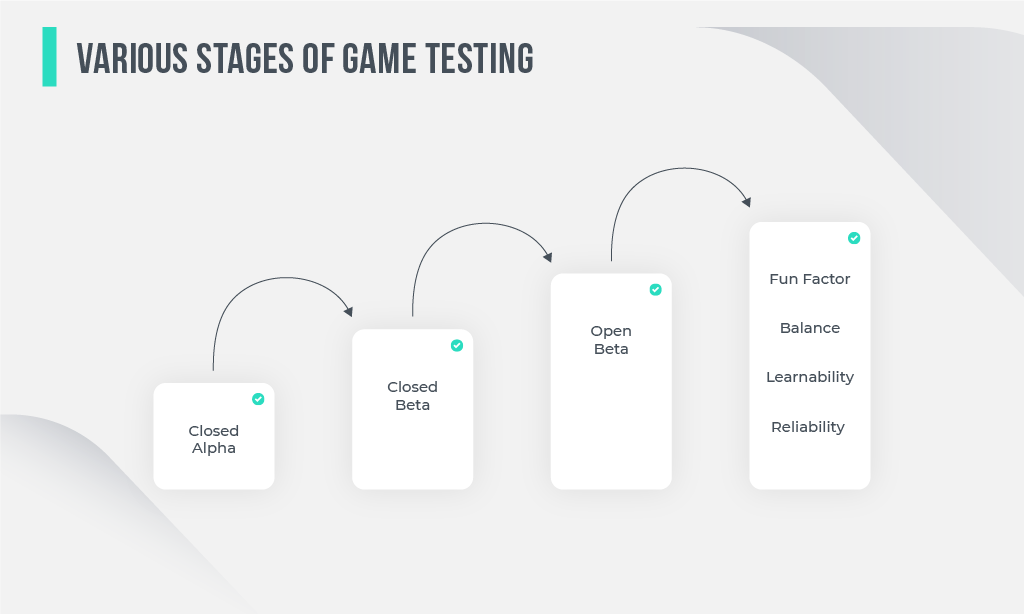
All the stages involve game testing processes delivered both by QA engineers and real players. We propose to follow every stage for a better understanding of the whole procedure.
What does the process of game testing consist of?
Game testing processes align with a typical SDLC (software development lifecycle): the game is tested on aspects like endurance, performance, and engaging user experience. The following list presents the usual steps:
- Requirement elicitation – complete game understanding (scenario, characters, game mechanics, level completion concept, etc.) to create the most efficient game testing strategy;
- Game testing strategy – determines the following: preparation of a certain document specifying testing roadmap, how many checking cycles are planned, what types of testing should be performed, and what processes must be presented (bugs, code defects, level errors, or game scenario irregularities);
- Test cases design – each test case consists of different test inputs, conditions of their implementation, and outcomes available to be in focus;
- Game test cases – execution offers a possibility to find more bugs and errors;
- Test results record – presents all bugs found in a document;
- Defect log maintenance – categorizing all defects found for post-release maintenance.

What are the types and techniques of game testing?
Before commercial product release engineers work on finding bugs and errors, quality control may look like the following:
- If we want to know whether the product meets the specification requirements, the team performs functionality QA. It’s testing user interface (UI), making sure the game is user-friendly and all the mechanics work smoothly;
- Sometimes it’s necessary to check as many game situations as possible, in this case, combinatorial testing is applied (specialists generate more and more test cases);
- Spontaneous random testing with no plan or case list is called Ad Hoc testing. It’s implemented as Monkey testing (random inputs to test possible game failures) or Pair testing (two engineers work on one keyboard to test the app robustly);
- Confirming whether the game works well on any device with any OS compatibility;
- Cleanroom and tree testing for checking code clarity;
- If after fixing the bus, it’s worth tracking whether errors occur or not in the same situations, regression testing is performed to run the past test cases;
- When the team tests an overall game, it is performance testing.

QA is applied practically on every stage of SDLC, being composed of many processes and performed in a variety of manners. It can be done either manually or in an automated way. What’s better?

Manual or Automation: What’s best for game testing?
Sometimes the game is tested manually, sometimes the tech team writes special scripts to automate quality control. Both methods have pros and cons.
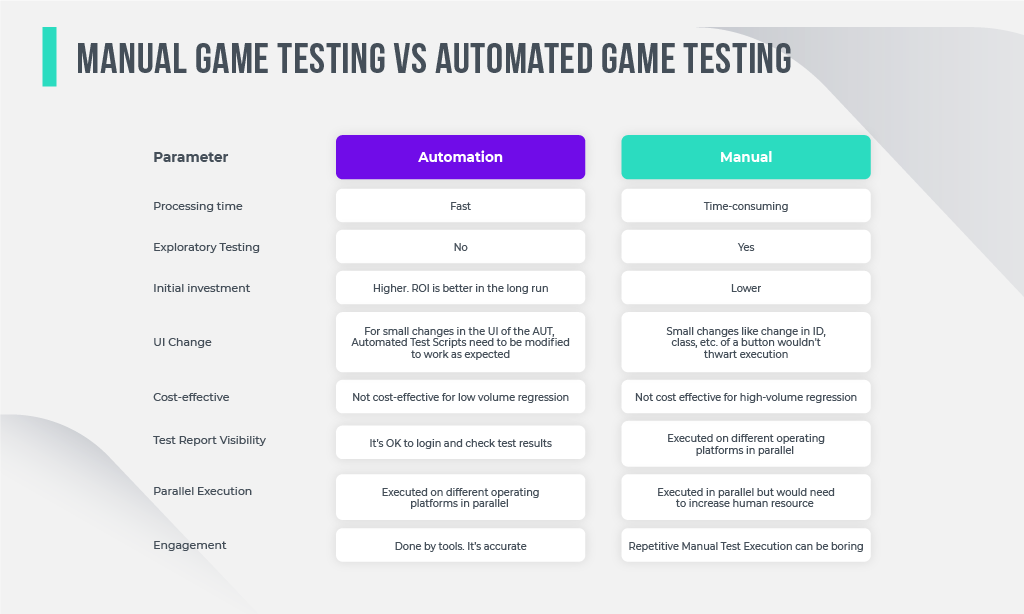
Manual testing is convenient because it provides:
- Accurate visual feedback;
- No need to budget for design automation tools;
- Human experience and intuition always contribute to the testing process;
- When testing small changes there is no need to write a whole new test, which can be time-consuming.
Automated QA:
- Time efficient, able to find more errors in the same period;
- Recorded thoroughly, it’s possible to perform the same testing again and again;
- Supports a variety of applications;
- It has wider coverage; automated tools can check the tiniest units.
To get the best of both worlds, human ingenuity and automation precision, sometimes it’s necessary to conduct both forms of testing. Exacol, a database developer, estimates manual testing is 100,000 times slower than automation. They suppose that automating repetitive tasks anywhere in development is prudent, but especially in testing. Consider the pros and cons of both methods for your project, just like we do for our clients at Innovecs.
How long does it take to test a game?
When estimating testing duration, keep in mind that every character must face every other character in every possible game situation on every possible level. It sounds quite time-consuming. Many repetitions are required, testers must play the whole game but also repeat the same game fragment trying to break it. Time should be spent finding code irregularities, art glitches, level bugs, and logic game errors.
Your testing process includes:
- Identifying incorrect software operation;
- Reporting the bug in the defect tracking system;
- Checking: artist, programmer, level designer research the defined malfunction;
- Verifying: after the developer spends time fixing the bug, the tester must prove an error doesn’t occur again.
To stick to deadlines, testing plans with detailed objectives, resources, and processes are helpful. You can estimate potential testing timeframe by considering previous experience with similar games, your knowledge about the testing processes, and awareness of how much time manual or automated testing requires. The more you know about QA, the easier it is to visualize the process and plan any necessary outsourcing.
Common Types of Bugs That Will Help You in Game Testing
The fact that Sony, a giant in the game industry, announced a global Bug Bounty Program is proof enough that it’s worth paying attention to testing if you want to produce a profitable product. Companies seeking opportunities to provide an engaging experience for their user community should test often to ensure perfect quality.
Let’s peek at some frequently found bugs:
- Graphic glitches, wrong image displayed, can look like this screenshot from Sims 4 (a comedic one);
- Gameplay defects: certain game functions not working as planned;
- Freezing, hanging, or crashing;
- In-game purchase problems: missing necessary payment options or overly complicated buying process;
- Audio defects are important to fix as the right audio and music create the mood of the game;
- Text problems: wrong, poor grammar, not aligned, or missed text options;
- Game save glitch: one of the most upsetting for players because of time and money investment.
Carefully considering every detail of testing issues can help avoid a failure after release. A bad release can destroy the reputation of the game production company and deter users from attempting any future game releases.
Conclusion
In this article we have outlined and described the following:
- QA is a substantial and critical part of SDLC, lack of thorough testing leads to game quality losses;
- Testing comprises numerous processes aimed at identifying, reporting, analyzing, and verifying bugs;
- Quality control can be performed in different manners depending on the objectives (retesting the same case, comparative analyses, or pair breaking);
- Manual testing is more about expertise, human intuition, and precise checking while automation is about wide coverage and time efficiency;
- To estimate testing time duration, it’s best to use a testing plan.
When you are ready to outsource testing, Innovecs can provide intuitive QA engineers who can protect your game from the risk of failure. They are well-versed in executing a variety of test cases to deal with bottlenecks and prevent financial losses due to poor game code. We are a trustworthy partner, and our QA experts implement up-to-date tech solutions.